|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a disease of the human immune system caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This condition progressively reduces the effectiveness of the immune system and leaves individuals susceptible to opportunistic infections and tumors. HIV is transmitted through direct contact of a mucous membrane or the bloodstream with a bodily fluid containing HIV, such as blood, semen, vaginal fluid, preseminal fluid, and breast milk. This transmission can involve anal, vaginal or oral sex, blood transfusion, contaminated hypodermic needles, exchange between mother and baby during pregnancy, childbirth, breastfeeding or other exposure to one of the above bodily fluids. Since AIDS was first identified in the early 1980s, an unprecedented number of people have been affected by the global AIDS epidemic. Today, there are an estimated 33.3 million people living with HIV and AIDS worldwide.
|
||||||||||||||||||
Causes of AIDS: |
||||||||||||||||||
HIV causes aIDS. HIV is a virus that gradually attacks immune system cells. As HIV progressively damages these cells, the body becomes more vulnerable to infections, which it will have difficulty in fighting off. It is at the point of very advanced HIV infection that a person is said to have AIDS. It can be years before HIV has damaged the immune system enough for AIDS to develop. |
||||||||||||||||||
Symptoms of AIDS: |
||||||||||||||||||
A person is diagnosed with AIDS when they have developed an AIDS related condition or symptom, called an opportunistic infection, or an AIDS related cancer. The infections are called ‘opportunistic’ because they take advantage of the opportunity offered by a weakened immune system. It is possible for someone to be diagnosed with AIDS even if they have not developed an opportunistic infection. AIDS can be diagnosed when the number of immune system cells (CD4 cells) in the blood of an HIV positive person drops below a certain level. |
||||||||||||||||||
Cure for AIDS: |
||||||||||||||||||
Worryingly, many people think there is a 'cure' for AIDS - which makes them feel safer, and perhaps take risks that they otherwise wouldn't. However, there is still no cure for AIDS. The only way to stay safe is to be aware of how HIV is transmitted and how to prevent HIV infection. |
||||||||||||||||||
Figure of died people from AIDS: |
||||||||||||||||||
Since the first cases of AIDS were identified in 1981, more than 25 million people have died from AIDS. An estimated 1.8 million people died as a result of AIDS in 2009 alone. |
||||||||||||||||||
Treatment of AIDS: |
||||||||||||||||||
Antiretroviral treatment can prolong the time between HIV infection and the onset of AIDS. Modern combination therapy is highly effective and someone with HIV who is taking treatment could live for the rest of their life without developing AIDS. It is also important that treatment is provided for AIDS related pain, which is experienced by almost all people in the very advanced stages of HIV infection. |
||||||||||||||||||
Caring of person from AIDS: |
||||||||||||||||||
In the later stages of AIDS, a person will need palliative care and emotional support. In many parts of the world, friends, family and AIDS organisations provide home-based care. This is particularly the case in countries with high HIV prevalence and overstretched healthcare systems. End of life care becomes necessary when a person has reached the very final stages of AIDS. At this stage, preparing for death and open discussion about whether a person is going to die often helps in addressing concerns and ensuring final wishes are followed. |
||||||||||||||||||
Situation of HIV / AIDS in Bihar: |
||||||||||||||||||
Bihar is sitting on the time bomb of AIDS epidemic. It is revealed by recent surveys which show that the HIV prevalence rate in Bihar is about five times higher than what was believed to be and eight populous districts in the state are in grip of HIV epidemic. The survey conducted by Bihar State AIDS control society in all 38 districts in July 2005 and December 2005 has found the rate to be 0.53%. Most of the people detected are in the age group of 25 to 45 years. The situation is alarming as it Bihar is one of the poorest states in the country and hence among the biggest suppliers of migrant labours. Whether it is seasonal farm hands for Punjab or construction workers for the skyscrapers in Mumbai and Delhi or new suburbs the daily wagers are supplied by Bihar. |
||||||||||||||||||
HIV Scare: |
||||||||||||||||||
A prevalence rate of 0.53% suggests NACO's projection of 0.13% was grossly undervalued. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
National Rate- 0.9% | State Rate- 0.53% |
||||||||||||||||||
These districts are among the poorest in Bihar and have huge migrant population. Most of the districts also share borders with Nepal. The high prevalence rates are direct fallout of the extreme poverty of these districts and the high migration rates. Due to lack of employment opportunities most men in rural Bihar migrate to Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat, Maharashtra and other states to work as laborers and spread the infection to their wives in the villages. According to the officials the remotest villages in every district were chosen to get genuine figures among the rural population. Samples found positive were tested twice to get confirmed figures. BSACS believes that the rate at which the infection is spreading very soon will cross the 1% prevalence rate. |
||||||||||||||||||
AIMYM imparts a number of programs in the topic of HIV/AIDS that includes HIV /Family education & substance abuse. According to National AIDS Control Organization (NACO), there are around 2.5 million people affected by HIV/AIDS in India. If not curbed, India could come at par with the countries of sub-Saharan Africa that are worst affected with HIV/AIDS. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
All these programs will not be success without your help, guidance and patronage. So, please help us, Allah will sure help you. DONATE PLEASE |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||








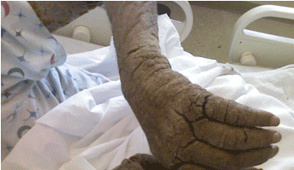 AIDS is now a pandemic As of 2009, AVERT estimated that there are 33.3 million people worldwide living with HIV/AIDS, with 2.6 million new HIV infections per year and 1.8 million annual deaths due to AIDS. In 2007, UNAIDS estimated: 33.2 million people worldwide had AIDS that year; AIDS killed 2.1 million people in the course of that year, including 330,000 children, and 76% of those deaths occurred in sub-Saharan Africa. According to UNAIDS 2009 report, worldwide some 60 million people have been infected, with some 25 million deaths, and 14 million orphaned children in southern Africa alone since the epidemic began.
AIDS is now a pandemic As of 2009, AVERT estimated that there are 33.3 million people worldwide living with HIV/AIDS, with 2.6 million new HIV infections per year and 1.8 million annual deaths due to AIDS. In 2007, UNAIDS estimated: 33.2 million people worldwide had AIDS that year; AIDS killed 2.1 million people in the course of that year, including 330,000 children, and 76% of those deaths occurred in sub-Saharan Africa. According to UNAIDS 2009 report, worldwide some 60 million people have been infected, with some 25 million deaths, and 14 million orphaned children in southern Africa alone since the epidemic began.